Whole-Genome Genotyping
Introduction to Whole-Genome Genotyping
Whole-genome genotyping, also known as genome-wide genotyping, provides an overview of the entire genome, enabling genome-wide discoveries and associations. Using high-throughput next-generation sequencing (NGS) and microarray technologies, researchers can obtain a deeper understanding of the genome, providing insight into the functional consequences of genetic variation.
Microarray-based genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been the most common approach for identifying disease associations across the whole genome. While whole-genome microarrays can interrogate over 4 million markers per sample, NGS-based whole-genome sequencing provides a comprehensive base-by-base method for interrogating the 3.2 billion bases of the human genome. Each technology offers unique advantages in price, data analysis, and throughput depending on particular study goals.
Advantages of Genome-Wide Genotyping
- Provides the most comprehensive view of the genome
- Detects single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and other variations across the genome
- Can identify potential causative disease variants for further targeted studies
- Expands range of discovery as content limitations are minimized

Human Whole-Genome Arrays
Whole-genome genotyping microarrays have been used to successfully identify regions of the human genome that contribute to disease susceptibility and phenotypes. Illumina human whole-genome arrays offer informative content for a variety of human genotyping applications, from GWAS to copy number variation analysis and more.

Array and Library Prep Kit Selector
Find and compare human whole-genome genotyping arrays with this easy-to-use tool.
Find the Right ArrayAll Illumina Arrays
View a full list of arrays, including kits designed for human genome-wide genotyping studies.
See All Array KitsCustom Genotyping
Design a genotyping array that focuses on your specific targets of interest.
Learn MoreFeatured Genotyping Research
Genetics of COVID-19 Susceptibility
Illumina is providing sequencing for a UK-wide study led by Genomics England, designed to compare the genomes of severely and mildly ill COVID-19 patients.
Read ArticlePharmacogenomics and Cardiovascular Disease
Researchers use an Illumina array to identify responder genotypes in a cholesterol drug trial.
Read InterviewGenome-Wide Genotyping Studies in Hispanic Populations
A collaborative genotyping effort identifies disease-associated SNP markers prevalent in the Hispanic population.
Read InterviewGenome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
These studies use high-throughput approaches to quickly scan entire genomes of large groups to find genetic variants correlated with a trait or disease. Variants for diseases like Type 2 diabetes and Parkinson's Disease were discovered using GWAS, but many opportunities remain.
Learn More about GWAS
Non-Human Whole-Genome Genotyping with Arrays
Illumina offers a comprehensive suite of genome-wide genotyping array products for non-human organisms. Find ready-to-use solutions for crops, livestock, and model organisms, or genotype any species with our custom array options.

Array and Library Prep Kit Selector
Find and compare non-human whole-genome genotyping arrays with this easy-to-use tool.
Find Non-Human ArraysAll Non-Human Genotyping Kits
Access a wide variety of kits, including arrays, for genotyping non-human species such as crops, livestock, and model organisms.
See All Agrigenomics KitsCustom Genotyping
Design custom arrays for any species or population, including those not supported by standard products.
Learn MoreNGS to Identify Novel Variants
While arrays are effective for assaying known variants, they are limited in detecting novel variants. NGS is an unbiased approach to variant detection that evaluates all loci and alleles regardless of prior expectations. Whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing are common approaches for finding causal variants for rare or complex disease studies.
Learn more about:
- Whole-Genome Sequencing: Characterize entire genomes of any size and complexity.
- Whole-Exome Sequencing: Sequence protein coding regions, as a cost-effective alternative to whole-genome sequencing
Understanding Human Genome Variation
Hear Dr. Tuuli Lappalainen discuss integrating genome and transcriptome sequencing data to understand functional variation in human genomes.
Adding Novel Variants to Arrays
Novel variants discovered using NGS can be used to generate a completely custom array, or added as additional content to an existing whole-genome genotyping array for large sample screening studies. Design custom panels targeting specific traits and/or genes of interest or for species and populations not available as standard panels.
Explore Custom Genotyping
Related Solutions
Large-Scale Genotyping

High throughput microarrays help labs identify common genetic variations among large cohorts for population-scale genotyping studies. Learn more about high-throughput genotyping.
Complex Disease Causal Variants
Screen large sample numbers quickly to find causal variants associated with complex diseases. Learn more about causal variant discovery.
Plant and Animal Genotyping

Enhance the value of crops and herds with screening and discovery tools that aid in breeding decisions. Learn more about plant and animal genotyping.
Genomics News

The next generation is shaping the future of rare diseases
Youth advocates such as Liam McCarthy are ensuring their voices are included in global conversations
Read article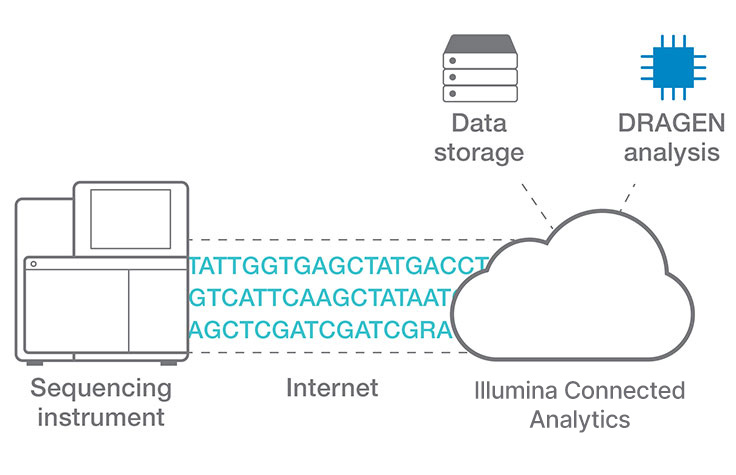
Efficient cloud data analysis for COPD multiomics project
Researchers at Okayama University in Japan use Illumina Connected Analytics with DRAGEN pipelines for analyzing whole-genome, exome, transcriptome, and metagenome data
Read Interview
The future of global food security may depend on quality agrigenomics software
In Hasselt, Belgium, Breed Bio’s next-level LIMS is reimagining the user experience and improving agriculture
Read articleInterested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on sequencing methods? Enter your email address.
Additional Resources
Microarray Data Analysis
Tools designed to facilitate analysis of microarray data and ensure optimal time-to-answer.
Sequencing Data Analysis
Easily analyze, store, manage and track genomic data with push-button bioinformatics tools.
Genomic Services
Access a diverse portfolio of array and NGS services that support a broad range of genetic analysis applications.
iScan Array Scanner
This cutting-edge array scanner offers industry-leading data quality and the flexibility to study any genetic variation.
Genomics Consortia
Explore consortium-built products that support high-throughput, multiplex studies of diverse populations and complex diseases.

