Genotyping by Sequencing
Introduction to Genotyping by Sequencing
Historically, array-based approaches to single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) screening have been the method of choice in analyzing and associating traits with regions of the genome for many plants and animals. As sequencing costs continue to decline, researchers are developing new approaches that leverage next-generation sequencing (NGS) for genotyping.
Genotyping by sequencing, or next-generation genotyping, is a genetic screening method for discovering novel plant and animal SNPs and performing genotyping studies. For some applications, such as genotype screening and genetic mapping, sequence-based genotyping provides a lower-cost alternative to arrays for studying genetic variation.
Genotyping by Sequencing in 3 Simple Steps
Sequence predetermined areas of genetic variation over many samples with this comprehensive workflow solution.
Advantages of Genotyping by Sequencing
- Sequences predetermined areas of genetic variation over many samples
- Provides a low cost per sample for certain applications
- Reduces ascertainment bias compared to arrays
- Identifies variants other than SNPs, including small insertions, deletions, and microsatellites
- Enables comparative analyses across samples in the absence of a reference genome
- Informs genetic mapping, screening backcross lines, purity testing, constructing haplotype maps, association mapping, and genomic selection for plant studies
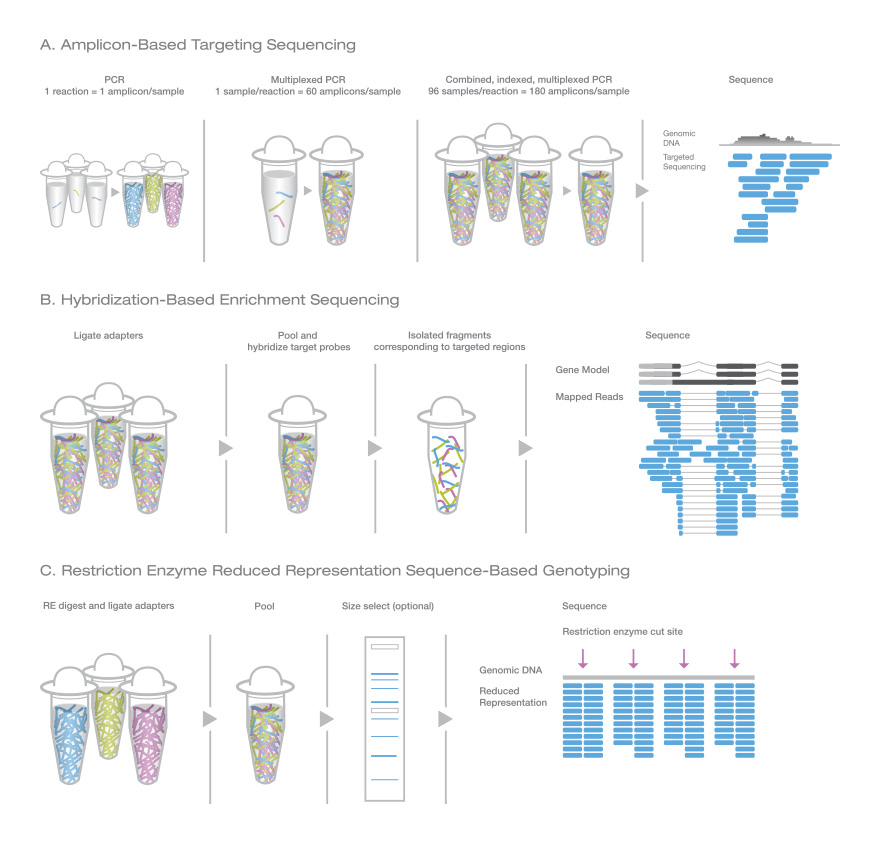
Genotyping by Sequencing for Large Genomes (> 5 Mb)
Genotyping by sequencing is cost-effective for populations with complex genomes or limited available resources. Techniques include amplicon-based targeted sequencing, hybridization-based enrichment sequencing, and restriction enzyme reduced representation sequence-based genotyping.
- A reference genome
- High-diversity samples
- Finely tuned coverage across multiplexed samples
- Variant call format (VCF) file converter
- Tolerance of ambiguity in heterozygote detection and redundancy checks to minimize false positives
Genotyping by Sequencing Methods
Various sequence-based genotyping approaches have been developed.1–4 Enrichment methods are useful for plants, which often contain duplicated areas of the genome. Restriction enzyme methods are advantageous for species where there is no prior knowledge of the genome.
Recommended Workflow for Genotyping by Sequencing
Data Analysis
Local Run Manager
An on-premises software solution for creating sequencing runs, monitoring run status, and analyzing data.
Featured Genotyping by Sequencing Research

Genotyping by Sequencing Enables Selective Breeding of Goat Herd
New Zealand–based research group uses GBS to overcome cost and resource hurdles associated with genomic selection for orphan crops and minor livestock species.
Read Interview
Revitalizing Fish Populations With NGS
Scientists developed Genotyping-in-Thousands by Sequencing (GT-Seq) to genotype thousands of fish simultaneously.
Read Interview
Genotyping by Sequencing Through Transcriptomics
The authors of this study used a genotyping by sequencing method based on transcript sampling to study crops with varying ploidy levels.
View PublicationGenotyping by Sequencing in Agrigenomics
For some applications, sequence-based genotyping provides a lower-cost alternative to microarrays in performing genetic variation studies. This application spotlight describes the advantages and limitations of several genotyping by sequencing methods.
Access PDF
Comprehensive Genotyping by Sequencing Workflow
Illumina sequencing by synthesis (SBS) chemistry is the most widely adopted NGS technology, generating approximately 90% of global sequencing data.*
Illumina offers integrated sequencing workflows that simplify the entire process, from library preparation to data analysis and biological interpretation.
Click on the below to view products for each workflow step.
Achieve consistent genotyping performance from content designed by Illumina Concierge services. Inquire about Illumina Concierge services.
Nextera XT DNA Library Prep KitLibrary preparation for small genomes (bacteria, archaea, viruses), amplicons, and plasmids in less than 90 minutes.
Determine the best kit for your needs based on project type, starting material, and method or application.
Speed and simplicity for targeted and small genome sequencing.
NextSeq 2000 SystemGroundbreaking benchtop sequencers allow you to explore new discoveries across a variety of current and emerging applications, with higher efficiency and fewer restraints.
NovaSeq 6000 SystemScalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
Compare sequencing platforms and identify the best system for your lab and applications.
Sequencing ReagentsFind kits that include sequencing reagents, flow cells, and/or buffers tailored to each Illumina sequencing system.
An on-premises software solution for creating sequencing runs, monitoring run status, and analyzing data.
BaseSpace BWA Aligner AppAligns samples (consisting of FASTQ files) to a reference genome.
BaseSpace Whole-Genome Sequencing AppQuickly extracts biological information from whole-genome sequences, using Isaac alignment and variant calling.
The Illumina genomics computing environment for NGS data analysis and management.
BaseSpace Correlation EngineA growing library of curated genomic data to support researchers in identifying disease mechanisms, drug targets, and biomarkers.
Genotyping by Sequencing for Small Genomes (≤ 5 Mb)
For small genomes (eg, Drosophila) or high-profile research species (eg, Arabidopsis), genotyping and variant screening can be completed using standard whole-genome sequencing or resequencing methods relative to a reference. Low-depth sequencing can be used for phylogenetic or comparative analyses.
Learn More
Related Solutions
Plant and Animal Sequencing

NGS technology can benefit agricultural studies of plants and animals, whether it is used for de novo sequencing, transcriptome analysis, genotyping by sequencing, or metagenomics. Learn more about plant and animal sequencing.
Commercial Agriculture

The application of genomics in commercial agriculture is helping breeders and researchers perform trait screening, parentage testing, and more. Learn more about commercial agriculture and genomics.
Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on genomic analysis techniques? Enter your email address.
References
- Mamanova L, Coffey AJ, Scott CE, et al. Target-enrichment strategies for next-generation sequencing. Nat Methods. 2010;7:111-118.
- Liu S, Yeh CT, Tang HM, Nettleton D, Schnable PS. Gene mapping via bulked segregant RNA-Seq (BSR-Seq). PLoS One. 2012;7:e36406.
- Cronn R, Knaus BJ, Liston A, et al. Targeted enrichment strategies for next generation plant biology. Am J Bot. 2012;99:291-311.
- Andolfatto P, Davison D, Erezyilmaz D, et al. Multiplexed shotgun genotyping for rapid and efficient genetic mapping. Genome Res. 2011;21:610-617.
*Data calculations on file. Illumina, Inc., 2015