NIPT Technology Types
Selecting a Type of NIPT Technology
The technology platforms commonly used for NIPT are whole-genome sequencing using next-generation sequencing (NGS) or various targeted methods. When looking at the best NIPT technology fit for your lab, you’ll want to consider data generation and analysis, lab workflow, and resulting clinical implications.
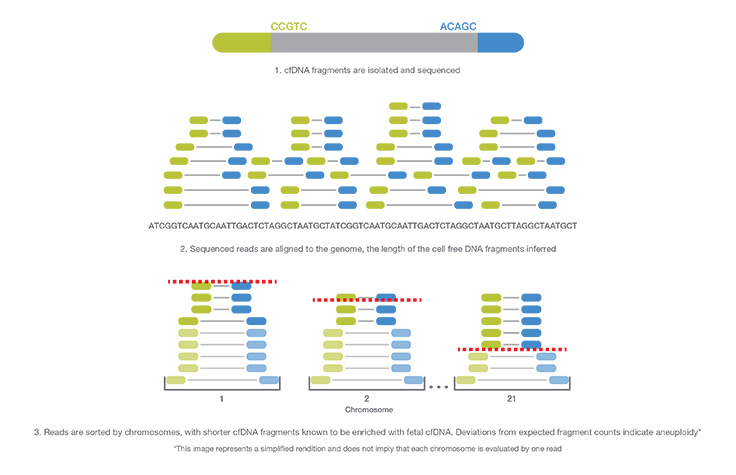
NIPT and Whole-Genome Sequencing
NIPT using whole-genome sequencing technology provides the most informative NIPT results1-7 with a comprehensive view across the entire genome. NIPT with whole-genome sequencing consistently has lower failure rates compared to targeted sequencing or array-based platforms8.
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-free sample preparation used with whole-genome-sequencing-based NIPT improves laboratory workflow, greatly reduces assay complexity and significantly improves turn-around time (TAT). This type of NIPT NGS technology can also be scaled easily to accommodate the needs of a growing lab.
Targeted Approaches for NIPT
Targeted technologies for NIPT include single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis, microarray analysis, and rolling circle amplification. With targeted approaches, only limited regions of select chromosomes are analyzed.
These targeted approaches have additional steps and employ more rounds of amplification than whole-genome sequencing methods, introducing a more complicated workflow.
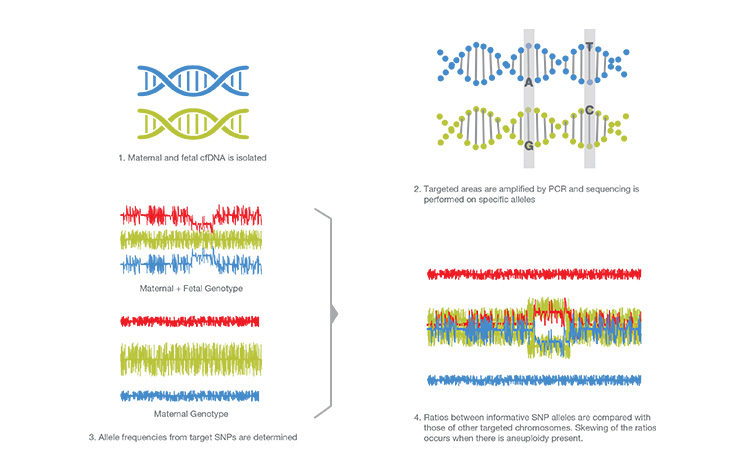
SNP Analysis
SNPs are genetic variations among individuals. This technique determines the difference between parent and child DNA, and the relative dosage of genetic variation to infer copy number. cfDNA is amplified by PCR using specific SNP targets. These targets are sequenced, and the allele distribution of both mother and child are determined. An algorithm determines abnormalities in expected allele frequencies.
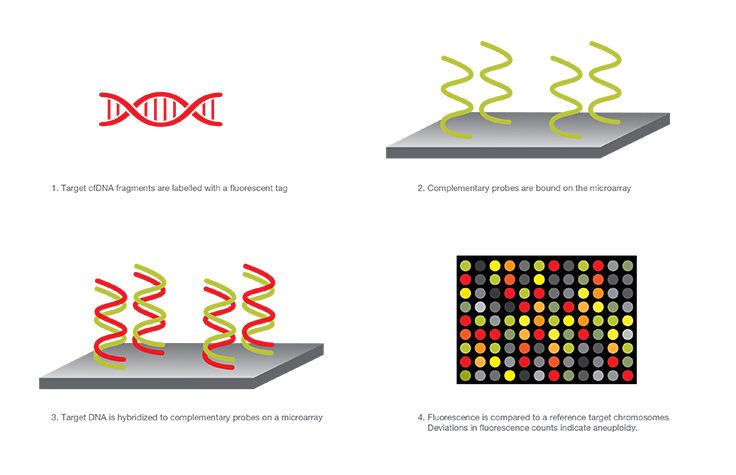
Microarray Analysis
In this type of NIPT, a microarray is used, which is an assembly of microscopic DNA regions attached to a solid surface. cfDNA fragments are amplified by PCR, tagged with a fluorescent probe, and bind to complimentary sequences on the NIPT microarray. Both the light intensity and binding position indicate the relative amount of DNA and presence or absence of the target, respectively. Deviations in expected fluorescent counts indicate aneuploidy.
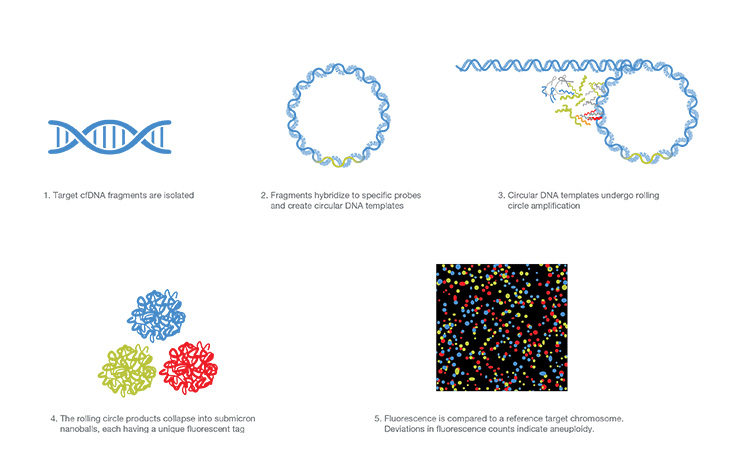
Rolling Circle Amplification
Rolling circle amplification targets specific cfDNA fragments which bind to a circular template and replicate by a rolling mechanism. The rolling circle replication products are fluorescently labeled and counted. Deviations in expected fluorescent counts indicate aneuploidy.
A Guide to NIPT Technology Options
Learn more about evaluating NIPT options and key considerations when selecting a technology for your lab.
Download GuideComparison of NIPT Technology Types
Additional Resources
The Science Behind NIPT
See how this NIPT workflow detects aneuploidy in three simple steps.
Noninvasive Prenatal Testing and NIPT
Dr. Wapner, Vice Chair of Research in Obstetrics and Gynecology for Columbia University, shares his perspective on prenatal screening and NIPT.
NIPT Delivers Relief to Expectant Mother
Whole-genome sequencing provides results when another test was inconclusive.
NIPT: Effective Screening for the General Pregnancy Population
Glenn Palomaki, PhD, discusses the clinical validity and utility of offering NIPT as a primary screen in the general pregnancy population.
References
- Illumina Inc. VeriSeq™ NIPT Solution v2 Package Insert. 2020
- Palomaki GE, Kloza EM, Lambert-Messerlian GM, et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma to detect Down syndrome: an international clinical validation study. Genet Med. 2011;13(11):913-920
- Ryan A, Hunkapiller N, Banjevic M, et al.Validation of an Enhanced Version of a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism-Based Noninvasive Prenatal Test for Detection of Fetal Aneuploidies. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2016;40(3):219-223.
- Stokowski R, Wang E, White K, et al. Clinical performance of non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) using targeted cell-free DNA analysis in maternal plasma with microarrays or next generation sequencing (NGS) is consistent across multiple controlled clinical studies. Prenat Diagn. 2015;doi: 10.1002/pd.4686.
- Jones KJ, Wang E, Bogard P, et al. Targeted cell-free DNA analysis with microarray quantitation for assessment of fetal sex and sex chromosome aneuploidy risk. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018;51(2):275-276.
- Taneja PA, Snyder HL, de Feo E, et al. Noninvasive prenatal testing in the general obstetric population: clinical performance and counseling considerations in over 85,000 cases. Prenat Diagn. 2016; doi:10.1002/pd.4766.
- McCullough RM, Almasri EA, Guan X, et al. Non-invasive prenatal chromosomal aneuploidy testing--clinical experience: 100,000 clinical samples.
- Data on file. Illumina, Inc. November 2018.