Infinium Methylation Assay
Infinium Methylation Assay Overview
The Infinium Methylation Assay provides quantitative array-based methylation measurement at the single-CpG-site level, offering high resolution for understanding epigenetic changes.
Genome-wide methylation analysis capabilities make this assay highly suitable for studying the biological role of DNA methylation in normal and diseased cells.
Powerful Infinium Chemistry
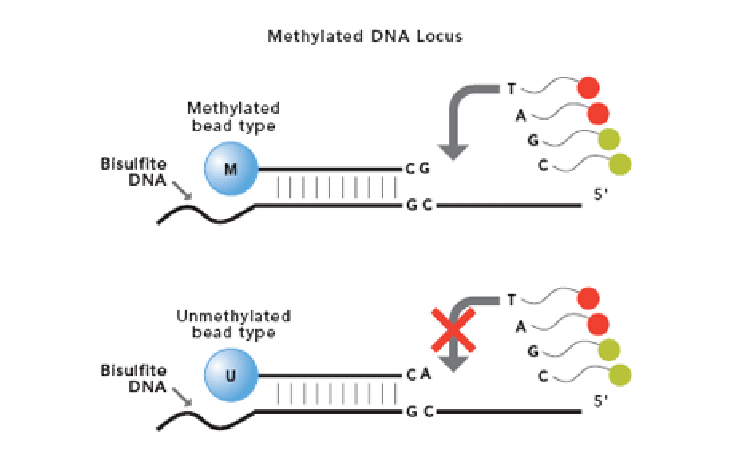
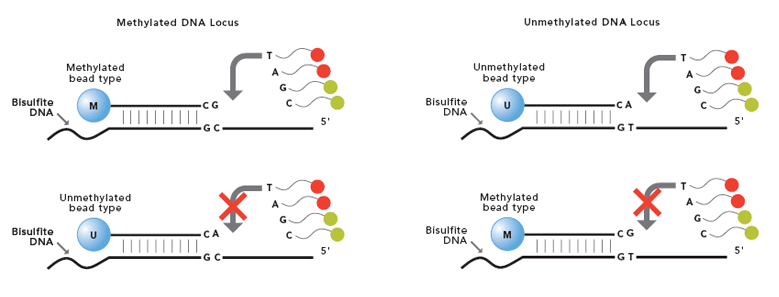
The Infinium Methylation Assay detects cytosine methylation at CpG islands based on highly multiplexed genotyping of bisulfite-converted genomic DNA. Upon treatment with bisulfite, unmethylated cytosine bases are converted to uracil, while methylated cytosine bases remain unchanged.
The assay interrogates these chemically differentiated loci using two site-specific probes, one designed for the methylated locus (M bead type), and another for the unmethylated locus (U bead type).
Single-base extension of the probes incorporates a labeled ddNTP, which is subsequently stained with a fluorescent reagent. The level of methylation for the interrogated locus can be determined by calculating the ratio of the fluorescent signals from the methylated vs. unmethylated sites.
The Infinium Methylation Assay is compatible with the iScan microarray imaging system.
Learn More About DNA Methylation AnalysisInfinium methylation microarrays: solutions for epigenetic researchers
Enhance your epigenetic research with the Infinium Methylation Microarrays guide. Learn how to integrate methylation data with other omics datasets to uncover complex biological interactions, identify disease biomarkers, and advance translational research with robust, scalable workflows.
Download Methylation Microarrays Guide
Featured Research Using Methylation Arrays

Exploring the Genetic Basis of Oral Cancer
Dr. Partha Majumder uses Illumina methylation arrays to look at epigenetic changes in oral cancer cases associated with chewing tobacco.
Read Interview
The Value of Panomics-Based Drug Discovery
The GLOBAL study integrates imaging, multiomic technologies, and big data, uncovering novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for common chronic diseases.
Read Interview
NGS Panels Demonstrate Value in Brain Tumor Studies
Learn why Se Hoon Kim, MD, PhD believes that comprehensive genetic profiling of brain tumors would benefit from methylation array analysis.
Read InterviewInfinium Methylation Assay Portfolio
Visit our Methylation Arrays page to learn more about the benefits of microarray-based methylation analysis and find products that utilize the Infinium Methylation Assay. These products offer comprehensive coverage of content categories selected by methylation experts, as well as custom options, providing an ideal solution for epigenetics studies.

Interested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information from Illumina based on your area of interest? Sign up now.
Related Solutions
Methylation Sequencing
Learn about the advantages of NGS-based methylation sequencing using whole-genome or targeted sequencing approaches.
Human Infinium DNA microarrays guide
This guide provides a detailed summary of arrays for genotyping, epigenetics, and cytogenetics research.