NTRK Fusions
NTRK fusion screening for cancer
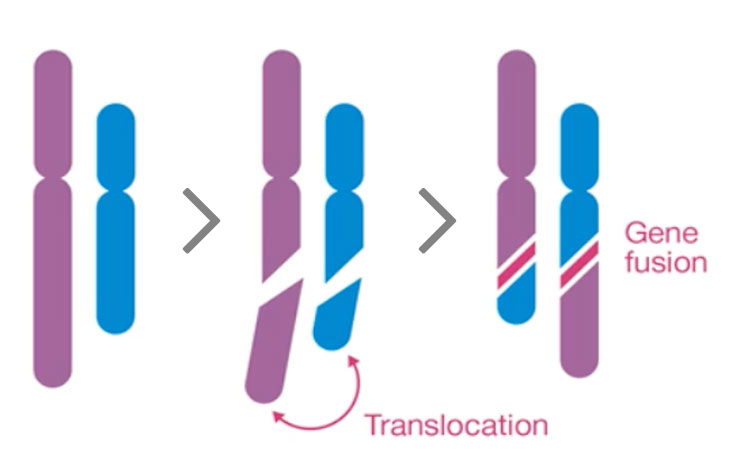
Gene fusions are detected in 15% of metastatic cancers regardless of cancer tissue lineage. Kinase fusions make up 35% of known fusions¹ and have been targeted by several new therapies, including therapies for fusions with the neurotrophic tyrosine kinase genes (NTRK1, NTRK2, and NTRK3).

Why NTRK fusions are important in cancer
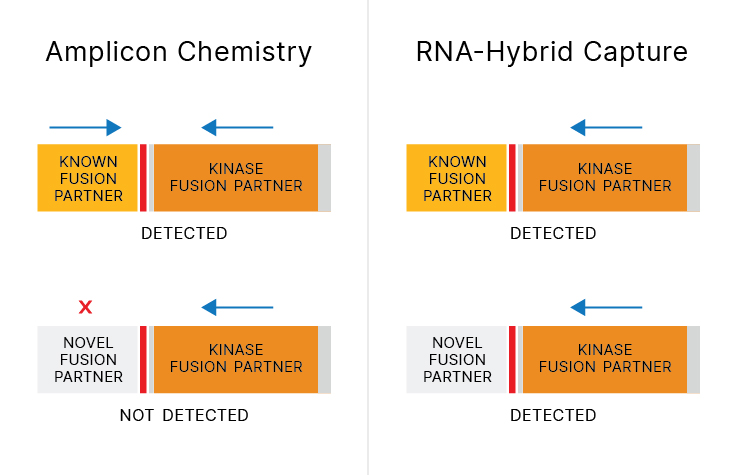
The diversity and complexity of NTRK biology has increased with frequent discovery of new fusion partners. Targetable kinase fusions show response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor, regardless of the fusion partner.2 Because NTRK fusion partners can be missed by commercially available amplicon-based NTRK detection assays3-5, comprehensive assays that detect novel fusion partners can provide value.
70% of NTRK fusion partners can be missed by commercially available amplicon assays. 3-5
NGS-based detection of novel NTRK fusions
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) assays that query RNA using hybrid-capture chemistry can capture novel NTRK RNA fusions. Without a priori knowledge in primer design, unknown fusion partners can be captured and sequenced—leading to new biomarker discoveries.

CGP enables analysis of RNA fusions of NTRK and many more genes in a single assay
The number of fusion-based biomarkers and targeted therapies in cancer are consistently increasing. Iterative testing for individual biomarkers can be challenging when time and sample are limiting. By consolidating relevant biomarkers into a single test, and using hybrid-capture chemistry to enable novel fusion detection, CGP can provide significant savings in sample, time, and cost.
Example NTRK workflow
Library Preparation
Sequencing
Data Analysis
Local Run Manager TruSight Oncology Comprehensive (EU) Analysis Module (On-Instrument Software)
*CE-marked IVD product
Comprehensive NTRK fusion detection
RNA-based hybrid-capture NGS enables the capturing of more NTRK fusions than DNA sequencing alone, agnostic of the fusion partner. Learn how Illumina NGS technology detects more fusions, including NTRK fusions.
NTRK fusion news and interviews

Matching patients with rare genetic mutations to targeted therapy
The Illumina TruSight Oncology Comprehensive (EU) test enables targeted therapy with Bayer's VITRAKVI® (larotrectinib) for patients with NTRK fusion cancer.

Testing for fusions with Vivek Subbiah, MD
Vivek Subbiah, MD, explains how patients with rare and common tumors can benefit from next generation sequencing-based testing for NTRK gene fusions.
Collaborating to evaluate the impact of in-house CGP to enhance patient care
Illumina and Allegheny Health Network to assess the efficacy of in-house testing for both tissue and blood samples and identify instances where blood-based testing is most beneficial.
References
- Zehir, et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Nat Med. 2017;23(6):703-713.
- Vitravki [package insert]. Stamford, CT: Loxo Oncology, Inc; November 2018.
- Hsiao SJ, Zehir A, Sireci AN, Aisner DL. Detection of tumor NTRK gene fusions to identify patients who may benefit from TRK inhibitor therapy. J Mol Diagn. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2019.03.008.
- OncomineTM Focus Assay, AmpliSeqTM Library page. https://www.thermofisher.com/order/catalog/product/A35957. Accessed February 14, 2019.
- St. James’s Hospital, Cancer Molecular Diagnostics Solid Tumour Service User Guide, http://www.stjames.ie/Departments/DepartmentsA-Z/C/CancerMolecularDiagnosticsLaboratory/DepartmentinDepth/User%20handbook%20v2.pdf. Accessed February 14, 2019.
- Cheng DT, Mitchell TN, Zehir A, et al. Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Proling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT): A hybridization capture-based next-generation sequencing clinical assay for solid tumor molecular oncology. J Mol Diagn. 2015;17(3):251-264.