Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-Seq)
What is ChIP-Seq?
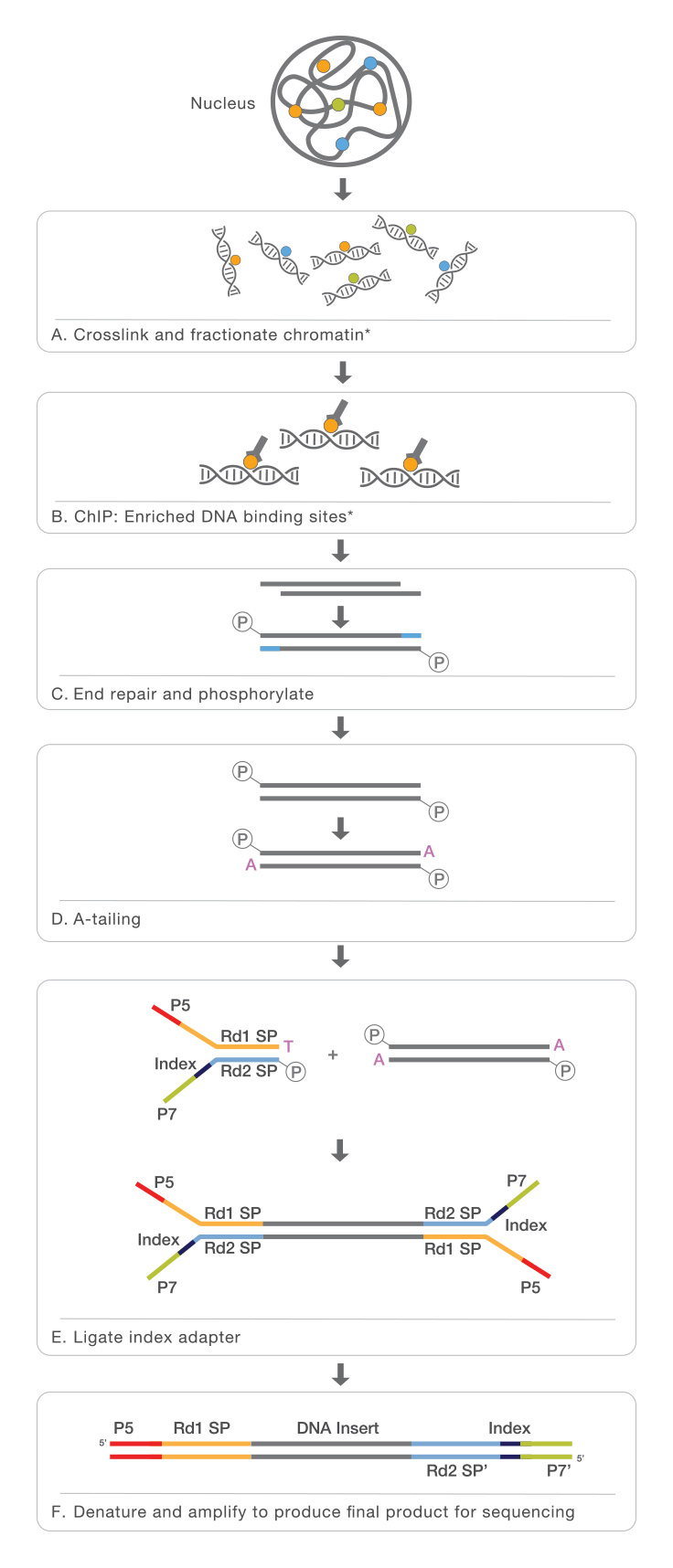
By combining chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays with sequencing, ChIP sequencing (ChIP-Seq) is a powerful method for identifying genome-wide DNA binding sites for transcription factors and other proteins. Following ChIP protocols, DNA-bound protein is immunoprecipitated using a specific antibody. The bound DNA is then coprecipitated, purified, and sequenced.
The application of next-generation sequencing (NGS) to ChIP has revealed insights into gene regulation events that play a role in various diseases and biological pathways, such as development and cancer progression. ChIP-Seq enables thorough examination of the interactions between proteins and nucleic acids on a genome-wide scale.
ChIP-Seq in 3 Simple Steps
Perform genome-wide surveys of gene regulation with this seamless workflow solution.
Advantages of ChIP-Seq
Unlike arrays and other approaches used to investigate the epigenome, which are inherently biased because they require probes derived from known sequences, ChIP-Seq does not require prior knowledge. ChIP-Seq delivers genome-wide profiling with massively parallel sequencing, generating millions of counts across multiple samples for cost-effective, precise, unbiased investigation of epigenetic patterns. Additional advantages include:
- Captures DNA targets for transcription factors or histone modifications across the entire genome of any organism
- Defines transcription factor binding sites
- Reveals gene regulatory networks in combination with RNA sequencing and methylation analysis
- Offers compatibility with various input DNA samples
How Does ChIP-Seq Work?
ChIP-Seq identifies the binding sites of DNA-associated proteins and can be used to map global binding sites for a given protein. ChIP-Seq typically starts with crosslinking of DNA-protein complexes. Samples are then fragmented and treated with an exonuclease to trim unbound oligonucleotides. Protein-specific antibodies are used to immunoprecipitate the DNA-protein complex. The DNA is extracted and sequenced, giving high-resolution sequences of the protein-binding sites.
Featured ChIP-Seq Research
NGS Proves Invaluable for Biomarker Discovery
Researchers use ChIP-Seq, RNA-Seq, and exome sequencing to study gene expression profiles associated with cancer and uncover biomarkers.
Read InterviewExploring the Unknown: NGS Supports Species Research

OIST researchers use Illumina NGS to sequence various ocean and land species. The institute offers a variety of services, such as de novo sequencing, ChIP-Seq, and RNA-Seq.
Read InterviewRecommended ChIP-Seq Workflow
Library Prep
TruSeq ChIP Library Prep Kit
Simple, cost-effective method for preparing sequencing libraries from ChIP-derived DNA.
Sequencing
NovaSeq 6000 System
Scalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
Analyze and interpret data
BaseSpace ChIPSeq App
Identify transcription factor binding sites using MACS2 and discover motifs within the peaks using HOMER.
Partek Flow
Detect and annotate peaks and compare across sample groups, identify enriched genes, discover motifs from regions, and explore the regulatory effect of transcription factors on gene expression by integrating ChIP-Seq analysis results with RNA-Seq data.
Comprehensive ChIP-Seq Workflow
Illumina offers integrated workflows that simplify chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing, from library preparation to data analysis and interpretation.
ChIP-Seq may require only a few reads (~5-15 million) for a highly targeted transcription factor, and many more reads (~50 million) for a ubiquitous protein such as a histone mark pull-down.
Click on the below to view products for each workflow step.
Simple, cost-effective method for preparing ChIP-Seq libraries from ChIP-derived DNA.
Groundbreaking benchtop sequencers allow you to explore new discoveries across a variety of current and emerging applications, with higher efficiency and fewer restraints.
NovaSeq 6000 SystemScalable throughput and flexibility for virtually any genome, sequencing method, and scale of project.
Compare Illumina sequencing platforms and identify the best system for your lab and applications.
Sequencing ReagentsFind kits that include sequencing reagents, flow cells, and/or buffers tailored to each Illumina sequencing system.
Identifies transcription factor binding sites using MACS2 and discovers motifs within the peaks using HOMER.
BaseSpace Sequence HubThe Illumina genomics computing environment for NGS data analysis and management.
A growing library of curated genomic data to support researchers in identifying disease mechanisms, drug targets, and biomarkers.
Partek FlowDetect and annotate peaks and compare across sample groups, identify enriched genes, discover motifs from regions, and explore the regulatory effect of transcription factors on gene expression by integrating ChIP-Seq analysis results with RNA-Seq data.
Related Solutions
Cancer Epigenetics
Studies of epigenetic changes in cancer, such as aberrant methylation and altered transcription factor binding, can offer insights into important tumorigenic pathways. Learn more about cancer epigenetics.
Gene Expression Analysis
Gene expression studies can provide visibility into how genomic and environmental changes contribute to various diseases. Learn how to profile gene expression.
Chromatin Accessibility Analysis

ATAC-Seq is a popular method for determining chromatin accessibility across the genome. Subsequent experiments often include ChIP-Seq, Methyl-Seq, or Hi-C-Seq. Learn more about ATAC-Seq.
Methylation Sequencing

NGS-based methylation sequencing approaches offer numerous benefits, including the ability to profile methylation patterns at a single nucleotide level. Learn more about methylation sequencing.
Cluster Density Tips
Optimal Cluster Density Best Practices
Watch Illumina scientists discuss how over- and underclustering can affect your sequencing data. Learn about common clustering issues and ways to prevent them.
View VideoHow to Achieve Consistent Cluster Density
Cluster density has a significant impact on run performance, specifically data quality and total output. Learn how to achieve more consistent cluster densities.
Read Knowledge ArticleFeatured Publications
Selective transcriptional regulation by Myc in cellular growth control and lymphomagenesis.
Researchers used Illumina sequencing to perform genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation and RNA expression profiling during B-cell lymphomagenesis.
Read PublicationRNA-Seq analysis and whole genome DNA-binding profile of the Vibrio cholerae histone-like nucleoid structuring protein (H-NS).
The authors used Illumina sequencing for differential RNA-seq and chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing using an anti-FLAG M2 monoclonal antibody.
Read PublicationChIP-Seq and Microarray Reveal a Sox9-Controlled Cancer-Specific Gene Network
Transcriptional profiling and in vivo ChIP-Seq studies uncover a cancer-specific gene network regulated by Sox9 that links tumor initiation and invasion.
Read PublicationInterested in receiving newsletters, case studies, and information on genomic analysis techniques? Enter your email address.
Additional Resources
Nature Epigenome Roadmap
The NIH Epigenome Roadmap highlights research characterizing epigenomic landscapes in primary human tissues and cells.
Blueprint Epigenome Project
Blueprint is a European research project that applies functional genomic analysis to understand the human epigenome.
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis
An overview of ChIP-Seq data processing using BaseSpace Correlation Engine.

ChIP-Seq Profiling of ERα Binding Sites
Researchers from Radboud University describe a ChIP-Seq method for analyzing estrogen receptor alpha binding sites.