High-Throughput Genotyping
The Power of Large-Scale Genotyping Studies
To realize the potential of precision medicine, genetic information must be amassed on a large scale. High-throughput genotyping studies are crucial for generating this volume of data and identifying disease associations. Currently, microarrays are the platform of choice for genotyping, as they allow investigators to survey millions of markers across disease cohorts or populations.
High-throughput genotyping data hold immense value for pharmacogenomics, consumer genomics, population studies, and clinical practice. These studies can identify not only genetic risk factors for disease, but also the genotypes associated with drug response. Eventually, this information can lead to better health management and more successful treatment strategies.
Benefits of High-Throughput Genotyping
Microarrays are ideal for large-scale genotyping studies to identify disease associations or characterize populations. Illumina arrays offer several advantages.
- Scalable workflow to support population studies or other large projects, with flexibility to increase throughput as demands grow
- Trusted data quality and widespread global adoption
- Low per-sample cost
- Integration with Illumina sequencing systems for multi-omics analysis
- Built-in lab management, tracking, and traceability tools to help production-scale and clinical labs ensure positive sample tracking
Pharmacogenomics and Cardiovascular Disease
Dr. Dubé and her team at the Montreal Health Institute used an array to identify responder genotypes in a cholesterol drug trial.
Read InterviewHigh-Throughput Genotyping Workflow
Featured Customer Stories

Bringing Meaning to Genetic Information
MyDNA partnered with Illumina, providing customers with access to its MyDNA software platform to make the most of the data produced and to enhance their reports.

Customizing Genetic Testing in Japan and Southeast Asia
Genesis Healthcare aims to help people make proactive lifestyle adjustments by offering direct-to-consumer kits based on the Infinium HumanCoreExome Array.
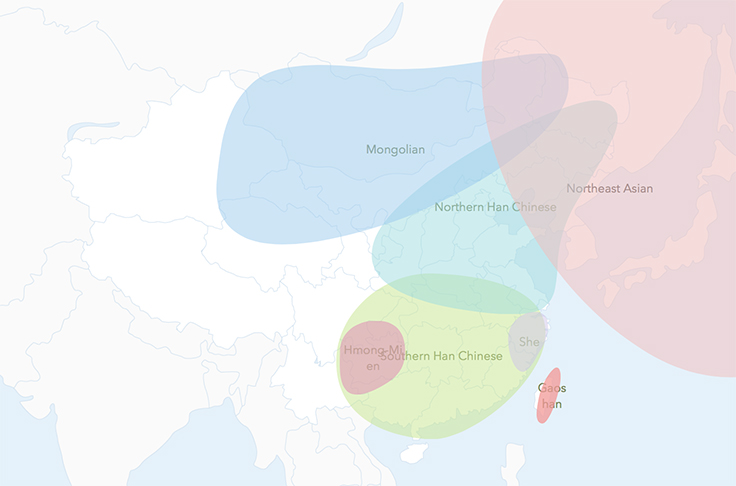
Development of an Ethnic Chinese Genome Database
High-throughput Infinium arrays help WeGene provide personal genetic testing services and support human genome research studies.
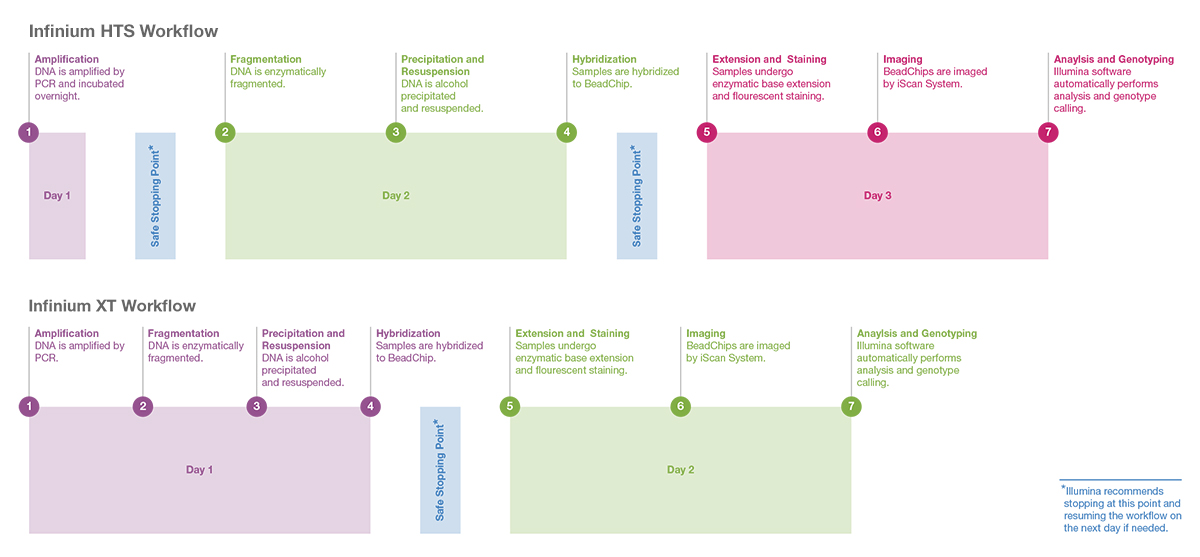
Rapid Microarray Workflow for High-Throughput Genotyping
The Infinium XT microarray workflow is ideal for production-scale genotyping, supporting biobanks and precision medicine initiatives. Each step of the Infinium workflow is optimized in the Infinium XT workflow, reducing the turnaround time from three days to two days.
Infinium Global Diversity Array with Enhanced PGx Content
Introducing the most comprehensive genotyping microarray on the market for pharmacogenomic (PGx) research with >1.9M markers, access to high-impact PGx genes, and optional reporting software with star allele calling and metabolizer status reporting.
Order Now

Prioritizing Functional Genetic Variants
Genome-wide association studies have identified thousands of variants with putative roles in different diseases and complex traits. However, going from statistical associations to true insight into mechanisms of disease or biology remains an incredible challenge for the field.
Powerful combinations of high-throughput experimental assays, single-cell approaches and computational analyses are accelerating the ability to link variants to function, and by extension, link genotype to phenotype.
View WebinarRelated Solutions
Complex Disease Genomics
Complex diseases result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Array and sequencing technologies can help reveal the underpinnings of these diseases.

Microarray Techniques
From discovery applications to routine screening, microarrays are a powerful tool for analyzing genetic variation.

Population Genomics
National population genomics programs seek to integrate large, diverse data sets, combining clinical information with genomic data at scale in a learning health system.